Résolution d'équation contenant des fractions rationnelles - Exemple 1
Résoudre l'équation 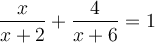 .
.
Le domaine est 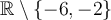 .
.
Résolution :
![\begin{array}{ll} \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{x+2} + \dfrac{4}{x+6} = 1 & \small\text{; on cherche le plus petit dénominateur commun}\\[0.5em] \Rightarrow \dfrac{x \left({x+6}\right) + 4 \left({x+2}\right) }{\left({x+2}\right) \left({x+6}\right)} = 1& {}\\[0.8em] \Rightarrow x \left({x+6}\right) + 4 \left({x+2}\right) = \left({x+2}\right) \left({x+6}\right)& \small{\text{; on peut multiplier, car } x \neq -2 \text{ et } x \neq -6 }\\[0.8em] \Rightarrow {x^2}+6x+4x+8 = {x^2}+8x+12 & {}\\[0.5em] \Rightarrow 2x = 4 & {} \\[0.5em] \Rightarrow x = 2 & {} \end{array} \begin{array}{ll} \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{x+2} + \dfrac{4}{x+6} = 1 & \small\text{; on cherche le plus petit dénominateur commun}\\[0.5em] \Rightarrow \dfrac{x \left({x+6}\right) + 4 \left({x+2}\right) }{\left({x+2}\right) \left({x+6}\right)} = 1& {}\\[0.8em] \Rightarrow x \left({x+6}\right) + 4 \left({x+2}\right) = \left({x+2}\right) \left({x+6}\right)& \small{\text{; on peut multiplier, car } x \neq -2 \text{ et } x \neq -6 }\\[0.8em] \Rightarrow {x^2}+6x+4x+8 = {x^2}+8x+12 & {}\\[0.5em] \Rightarrow 2x = 4 & {} \\[0.5em] \Rightarrow x = 2 & {} \end{array}](https://mathematic.moodle.decclic.qc.ca/filter/tex/pix.php/dacd5cd9f7c1924619abb55f1d5b68ee.png)
La solution trouvée est 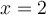 , car elle appartient au domaine
, car elle appartient au domaine 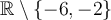 .
.
Vérification :
On remplace dans l'équation initiale : 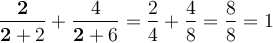 .
.
Modifié le: mercredi 10 février 2016, 00:45